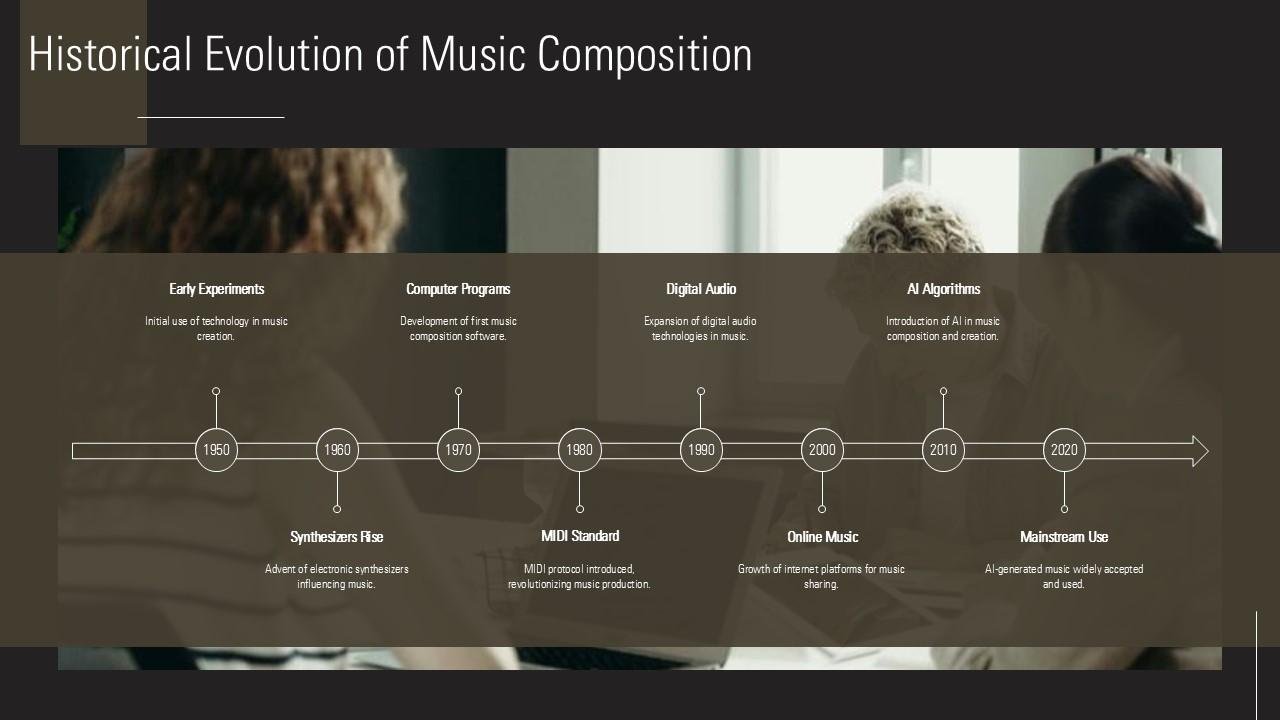
The Evolution of Music Composition Through the Ages
Music composition has undergone a fascinating evolution, reflecting societal changes, technological advancements, and the ever-changing tastes of listeners. From the chants of ancient civilizations to the experimental sounds of today, music composition serves as a mirror to humanity’s cultural and emotional journey.
1. Ancient Music: The Origins of Melody
- Period: Prehistoric to 500 CE
- Key Characteristics:
Music during ancient times was primarily vocal and served religious or ceremonial purposes. Instruments like flutes made of bone, lyres, and drums were used to accompany chants. - Influence:
Ancient Egyptians, Greeks, and Mesopotamians laid the groundwork for musical notation and scales. The Hymn to Nikkal and Greek modes showcased early structured compositions.
2. The Medieval Era: Birth of Western Music Theory
- Period: 500–1400
- Key Characteristics:
Gregorian chants dominated, characterized by monophonic texture (single melodic line). The development of neumes (early notation) allowed music to be written and preserved. - Notable Development:
Polyphony emerged, allowing multiple melodic lines to coexist, paving the way for more complex compositions.
3. The Renaissance Era: Harmony and Exploration
- Period: 1400–1600
- Key Characteristics:
Renaissance composers explored harmony, creating richer textures. Music shifted from being solely religious to also celebrating humanism. - Famous Composers:
- Josquin des Prez (Ave Maria)
- Palestrina (Missa Papae Marcelli)
- Impact:
Innovations in notation and printing made music more accessible, enabling composers to share their works widely.
4. The Baroque Era: Ornamentation and Grandeur
- Period: 1600–1750
- Key Characteristics:
Baroque music emphasized contrast, drama, and ornate detail. The invention of the basso continuo provided a harmonic foundation for compositions. - Famous Composers:
- Johann Sebastian Bach (The Well-Tempered Clavier)
- George Frideric Handel (Messiah)
- Antonio Vivaldi (The Four Seasons)
- Impact:
The establishment of tonal harmony (major and minor scales) shaped Western music for centuries.
5. The Classical Era: Elegance and Structure
- Period: 1750–1820
- Key Characteristics:
Classical music focused on clarity, balance, and form. The sonata form became a cornerstone of composition. - Famous Composers:
- Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (Symphony No. 40)
- Ludwig van Beethoven (Symphony No. 5)
- Franz Joseph Haydn (The Creation)
- Impact:
The orchestral symphony and piano sonata gained prominence, and composers began writing music for public concerts.
6. The Romantic Era: Emotion and Expression
- Period: 1820–1900
- Key Characteristics:
Romantic music celebrated individualism, nature, and intense emotion. Composers used chromatic harmonies and expanded orchestras to express their ideas. - Famous Composers:
- Franz Schubert (Ave Maria)
- Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky (Swan Lake)
- Richard Wagner (The Ring Cycle)
- Impact:
The rise of the virtuoso and nationalistic music movements reflected the spirit of the times.

7. The Modern Era: Innovation and Diversity
- Period: 1900–Present
- Key Characteristics:
Modern composers broke traditional rules, experimenting with atonality, electronic music, and minimalism. Genres like jazz, rock, and electronic music diversified the music landscape. - Famous Composers:
- Igor Stravinsky (The Rite of Spring)
- John Cage (4’33”)
- Hans Zimmer (Interstellar Soundtrack)
- Impact:
Advancements in technology, such as synthesizers and digital audio workstations, revolutionized music composition and production.
Conclusion
From the simplicity of ancient melodies to the complex soundscapes of today, music composition has been an ever-evolving art form. Each era brought new styles, techniques, and innovations that shaped the way we create and experience music. As technology and culture continue to progress, the future of music composition promises even greater creativity and diversity.